Not all kinds of neck pain occur due to spondylitis. You could be suffering from Trapezius as well. Here’s all that you need to know:
Neck pain is quite common among individuals of all age group. Initially, it was commonly found among the elderly and people with prolong reading and writing occupations. The most commonly learnt terminology for neck pain of any kind is ‘Spondylitis.’ It is often perceived that spondylitis is the cause behind your neck pain. But how can we define spondylitis in the lower age group or persons with acute onset? At present due to the random use of mobile phones and other gadgets, the incidents of neck pain has increased by three to four folds. Perhaps, we are heading back to the Stone Age with our posture and attitude. So, spondylitis is a chronic condition affecting the spine such as neck, upper and lower back in the form of pain, restricted movement and bony changes on X-rays.
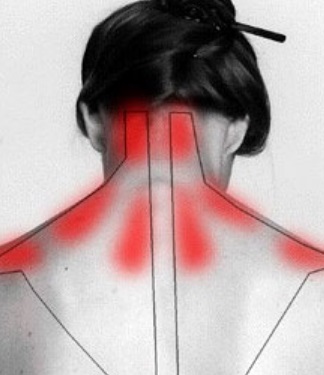
Most of the people generally complain of neck pain around the upper part of the neck (nape of neck) mid neck, shoulder and inter-scapular area. Neck pain can be of an isolated nature or a tingling sensation and heaviness of the bilateral or unilateral upper limbs. A pain, which is generated from the hand towards the neck, is separate from the pain around the neck towards the hands.
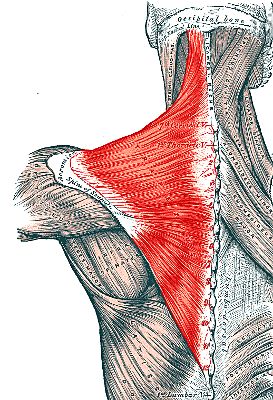
What is Trapezius?
Isolated neck pain with acute onset and non-radiating is typically muscular. The most common muscle involved is trapezius. Trapezius is a long muscle towards the back of neck which arises from the nape of neck till the upper back with extension towards the bilateral shoulders. The muscle performs various functions—like lifting of the head upwards and shrugging of the shoulders. The upper back muscles facilitate movement, rotation and stabilization of the shoulder blade. So, any inflammation of the neck muscles or trapezius can cause severe pain and also affect the related movements.
Causes of trapezitis
- Forward head posture
- Sitting for a prolonged period without back support
- Holding phone between head and shoulder
- Too high keyboard on desk
- Working with no arm support on desk
- Prolonged head bending activities like reading
- Stiff pectoralis major muscles
- Turning head to one side
- Sport activities with sudden one-side movement
Signs and symptoms
- Head on the base of head
- Pain behind the eye
- Neck pain
- Stiff neck pain
- Upper shoulder pain
- Limited range of motion
- Intolerance to weight on your shoulder
- Pain on the shoulder blades and down side of arm .
Management
It generally takes 1 to 2 weeks to subside by its own and If it is post traumatic then it will take 2 to 4 weeks . Apply ice 2 to 3 times a day for 10 minutes each in acute cases . Encourage active neck movements along the direction of pain. Avoid neck or cervical collar.
Physio therapy: Mainstay of the treatment
Medications such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxants are helpful. Physio therapy is mainstay of the treatment along with medications . Minimal isometric neck exercises with active or passive range of movement exercises along with release of trapezius muscles is required. Sometimes a neck mobilisation by an expert physiotherapist do helps a lot.