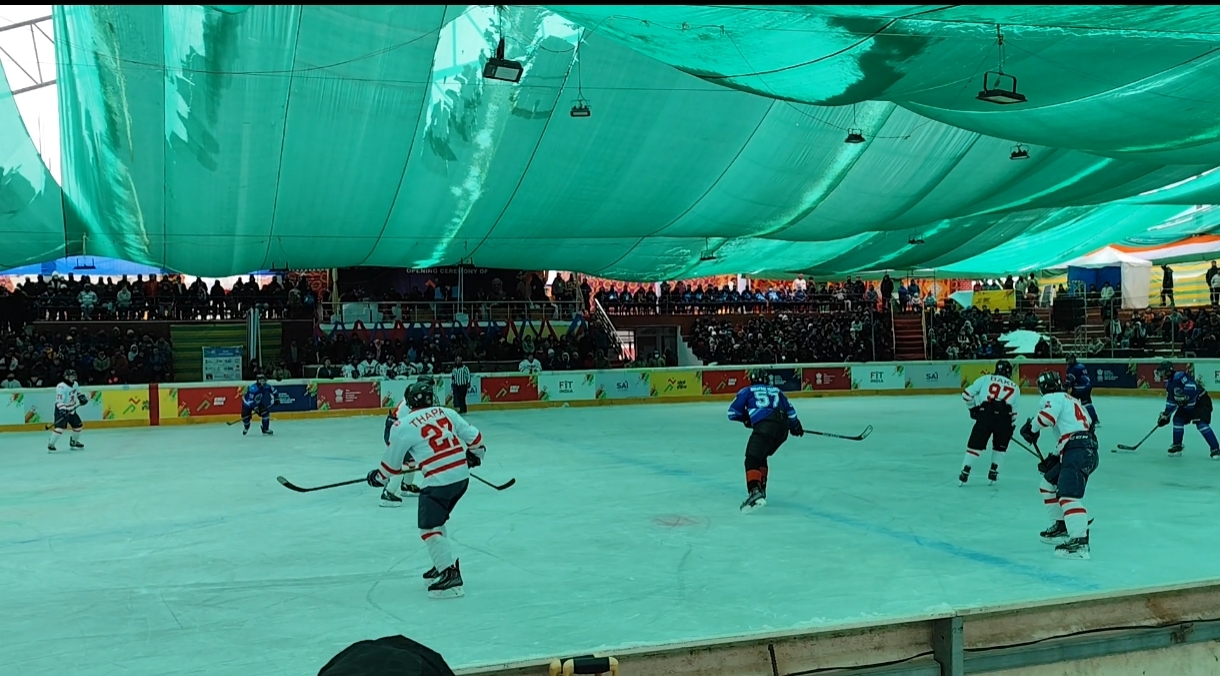
ditionally, proper technique, conditioning, and adherence to the rules regarding checking and body contact can help reduce the risk of injuries. Regular warm-up exercises, strength training and flexibility exercises can also contribute to injury prevention.
Concussions
It results from head trauma. Concussions can have serious consequences. Treatment involves rest, cognitive and physical rest, and gradual return to play protocols. Preventive measures include wearing properly-fitted helmets, enforcing rules against head contact, and educating players on safe play techniques.
Muscle strains & sprains
These injuries occur frequently due to sudden movements or collisions. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with physical therapy. Preventive measures include proper warm-up, stretching, and strength training to improve muscle flexibility and resilience.
Fractures
Fractures can happen at various parts of the body, including the wrists, ankles, and collarbones. Treatment typically involves immobilization with casts or splints and, in severe cases, surgery. Prevention includes wearing protective gear and avoiding dangerous collisions.
Laceration
Cuts and wounds from contact with skates, sticks, or the boards require cleaning, disinfection, and sometimes stitches. Prevention involves wearing cut-resistant equipment and avoiding reckless play near the boards or other players.
Overuse injuries
These include tendonitis, bursitis, and stress fractures, often caused by repetitive motions. Treatment involves rest, ice, physical therapy, and modifying activity levels. Prevention includes proper training techniques, adequate rest, and monitoring for signs of overuse.
Dental injuries
These can range from chipped teeth to more serious dental trauma. Treatment involves seeing a dentist for evaluation and possible dental work. Prevention includes wearing a mouth guard during play.
Eye injuries
These result from high-speed pucks or sticks. These can be severe. Treatment involves immediate medical attention, possibly including surgery. Prevention includes wearing a full-face shield or cage and being vigilant about safety on the ice.

Physiotherapy protocol
- Initial assessment: A physiotherapist assesses the injury to determine its severity and the best course of treatment. They may conduct physical examinations, review medical history, and sometime utilize imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans.
- Pain management: Usage of various techniques such as manual therapy, electrical modalities (e.g., ultrasound, TENS), and ice or heat therapy to manage pain and inflammation associated with injuries.
- Restoration of range of motion and strength: It involves exercises and techniques aimed at restoring normal range of motion and strengthening of injured muscles and joints. This may include stretching exercises, resistance training, and functional exercises tailored to the specific needs of hockey players.
- Balance and proprioception training: Since hockey requires excellent balance and proprioception, physiotherapists often incorporate specific exercises to improve these skills, reducing the risk of future injuries.
- Functional rehabilitation: Physiotherapists work on restoring functional abilities required for playing hockey, such as skating, shooting, and puck handling. This involves sport-specific drills and activities to gradually reintegrate players back into the game safely.
- Return to play protocols: Physiotherapists collaborate with coaches and medical staff to develop and implement return to play protocols. These protocols ensure that players only return to the ice when they’re fully recovered and at minimal risk of re-injury.
- Injury prevention strategies: Physiotherapists educate players on injury prevention strategies, including proper warm-up and cool-down routines, biomechanics, and equipment selection and fit.
- Post-surgical rehabilitation: In cases where surgery is necessary, such as repairing ligament tears or fractures, physiotherapists guide players through post-operative rehabilitation to optimize recovery and regain strength and function.